k8s-Cluster Maintenance
OS Upgrades
For example,you have a cluster with a few nodes and pods serving applications.If one of these nodes go down,the pods on that node are not accessible.
If the node came back online immediately,then the kubectl process starts and the pods come back.However,if the node was down for more than 5 mins,then the pods are terminated from that node.
pod eviction:
The time wait for a pod to come back.
Pod eviction is set on the controller manager
kube-controller-manager --pod-eviction-timeout=5m0s
When the node comes back online after the pod eviction timeout it comes up blank without any pods scheduled on it.
Maintenance a node

kubectl drain node-1:When you drain(放空,放干) the node the pods are gracefully terminated from the node that they’re on and recreated on another.
The node is also cordoned or marked as unschedulable. Meaning no pods can be scheduled on this node until you specifically remove the restriction.
kubectl uncordon node-1:Uncordon the node,so that pods can be scheduled on it again.
kubectl cordon node-2:cordon simply marks a node unschedulable. Unlike drain it does not terminate or move the pods on an existing node.It simply make sure than new pods are not scheduled on that node.
Practice
On which nodes are the applications hosted on?
Run the command
kubectl get pods -o wideand get the list of nodes the pods are placed onWe need to take
node01out for maintenance. Empty the node of all applications and mark it unschedulable.kubectl drain node01 --ignore-daemonsetsThe maintenance tasks have been completed. Configure the node to be schedulable again.
kubectl uncordon node01Why are there no pods placed on the
masternode?Use the command
kubectl describe node master/controlplaneNode03 has our critical applications. We do not want to schedule any more apps on node03. Mark
node03asunschedulablebut do not remove any apps currently running on it .kubectl cordon node03
kubernetes Release


alpha release: The features are disabled by default and maybe buggy.
beta release: The code is well tested.
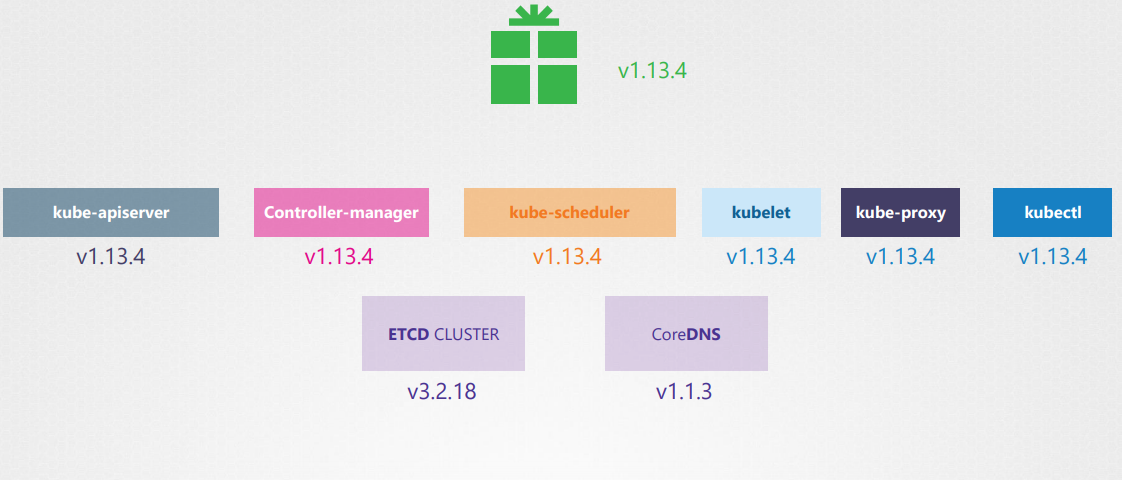
The ETCD and CoreDNS servers have their own versions as they are separate projects.
Cluster Upgrade Process
Component Version

The kube-apiserver is the primary component.
None of the other components should ever be at a version higher than the kube-apiserver the controller.
So if kube-apiserver was at X ,Controller-manager and kube-scheduler can be at X-1 and the kubelet and kube-proxy components can be at X-2.
Upgrade Step
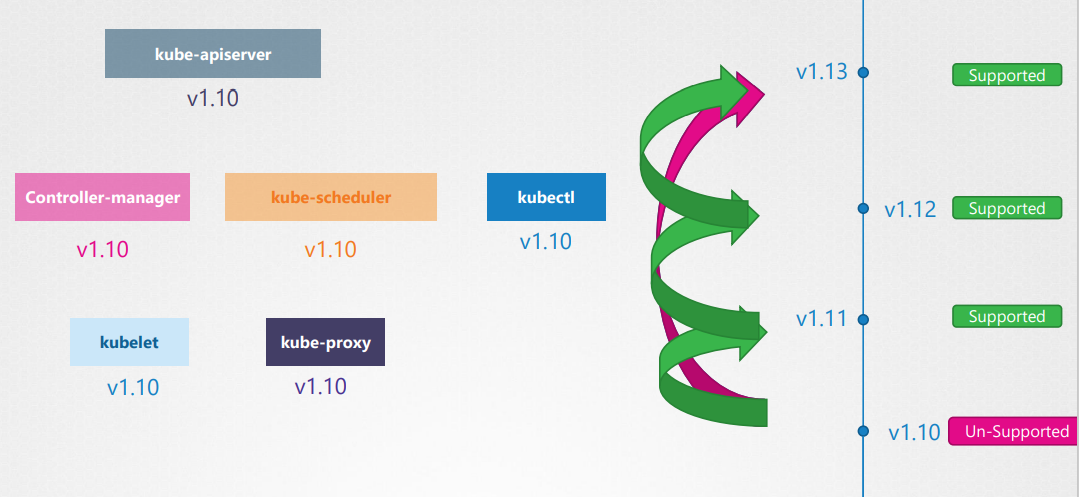
We cannot upgrade directly from 1.10 to 1.13. We should upgrade one minor version at a time.(v1.10 to 1.11 to 1.12 to 1.13.)
kubeadm upgrade
upgrade master node
kubeadm upgrade plan:Check the latest stable version available for upgrade
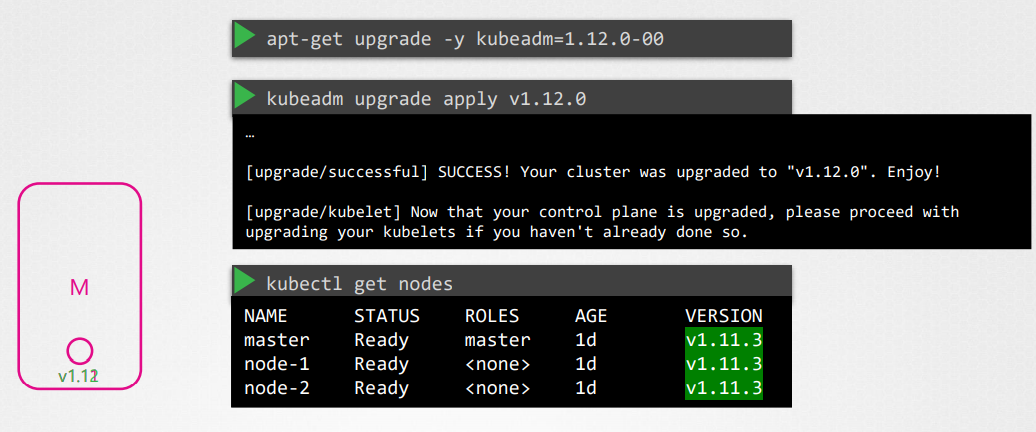
The master node version is still v1.11.3.
This is because in the output of this command it is showing the versions of kubelet on each of these nodes registered with the API server and not the version of the kube-apiserver itself.
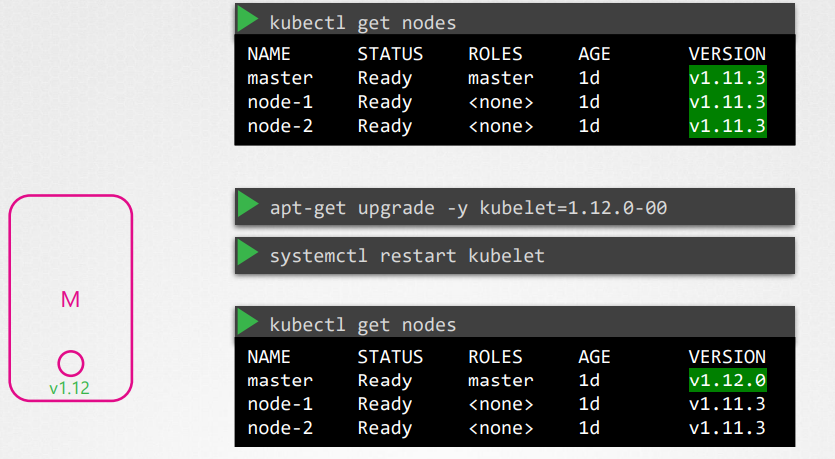
- Then upgrade
kubelet
upgrade worker node
upgrade node01
kubectl drain node01ssh node01apt-get upgrade -y kubeadm=1.12.0-00apt-get upgrade -y kubelet=1.12.0-00kubeadm upgrade nodesystemctl restart kubeletkubectl uncordon node-1

- node02 : same as the upgarde of node01
- node03
Practice
What is the latest stable version available for upgrade?Use
kubeadmtoolkubeadm upgrade planWe will be upgrading the master node first. Drain the master node of workloads and mark it
UnSchedulablekubectl drain master/controlplane --ignore-daemonsetsUpgrade the master/controlplane components to exact version
v1.19.0Upgrade kubeadm tool (if not already), then the master components, and finally the kubelet. Practice referring to the kubernetes documentation page. Note: While upgrading kubelet, if you hit dependency issue while running the
apt-get upgrade kubeletcommand, use theapt install kubelet=1.19.0-00command insteadapt updateapt install -y kubeadm=1.19.0-00kubeadm upgrade apply v1.19.0apt install -y kubelet=1.19.0-00systemctl restart kubelet
Backup and Restore Methods
Query kube-apiserver
A better approach to backing up resource configuration is to use query the kube-apiserver
use
kubectlto backup resourceskubectl get all --all-namespaces -o yaml > all-deploy-services.yaml
Backup - ETCD
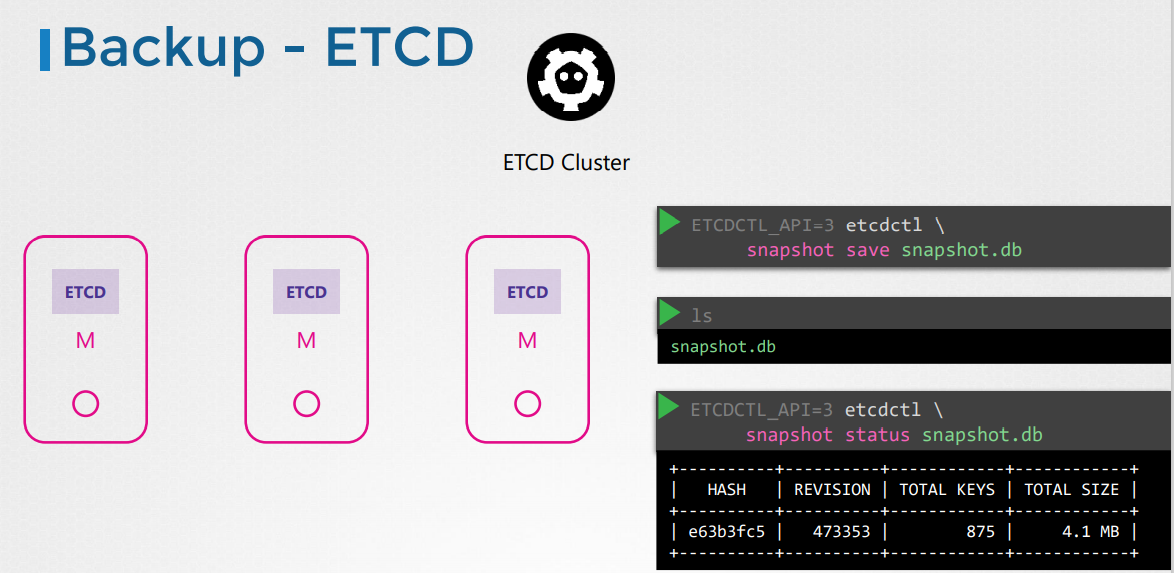
Take snapshot of etcd database (named snapshot.db)
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl snapshot save snapshot.dbView the status of the backup
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl snapshot status snapshot.db
Restore-ETCD
When ETCD restores from a backup, it initializes a new cluster configuration and configures the members of ETCD as new members to a new cluster.

Use
etcdctl restorecommandSet
--data-dir--initial-cluster-token:This is to prevent a new member from accidentally joining an existing cluster.